Launch a chatbot that runs inference on Modal using the Vercel AI SDK
Building a full-stack chatbot powered by Qwen 3 8B, Modal, and Vercel’s AI SDK requires just three steps:
Deploy the Qwen 3 8B model on Modal
Connect a Next.js app to Modal with the AI SDK
Add a chat UI with Vercel’s AI Elements
In five minutes, this chatbot with its swanky UI will be running on the web:
Setup
Let’s start with some project scaffolding:
1. Deploy the Qwen 3 8B model on Modal
In the Modal examples, there is a great tutorial for deploying the Qwen 3 8B on Modal. I stole that exact code to write this backend, so I recommend taking a look at the tutorial for a technical explanation.
In short, this code runs a vLLM server in OpenAI-compatible mode so that downstream clients and tools that know how to use the OpenAI API can interact with the server.
Since we’re on a time crunch, paste the following code in a python file named vllm-inference.py.
Now to deploy the API on Modal, make sure uv and Modal are installed and set up before running the Modal deploy command.
To install uv, run:
To install and setup Modal, run:
Now, to deploy the API on Modal, run:
Once your code is deployed, you’ll see a URL appear in the command line, something like https://your-workspace-name--example-vllm-inference-serve.modal.run.
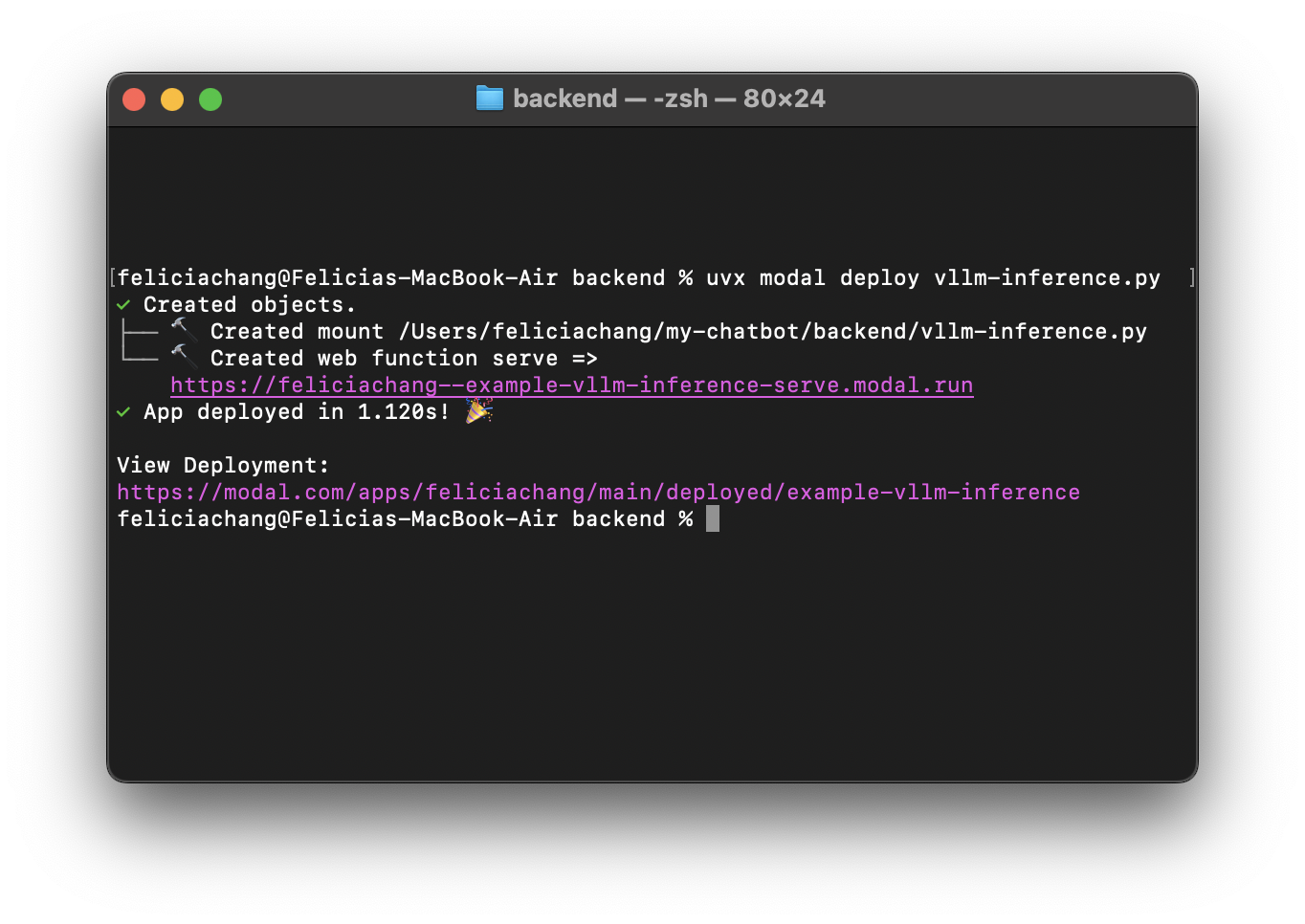
You can also find the URL on your Modal dashboard:
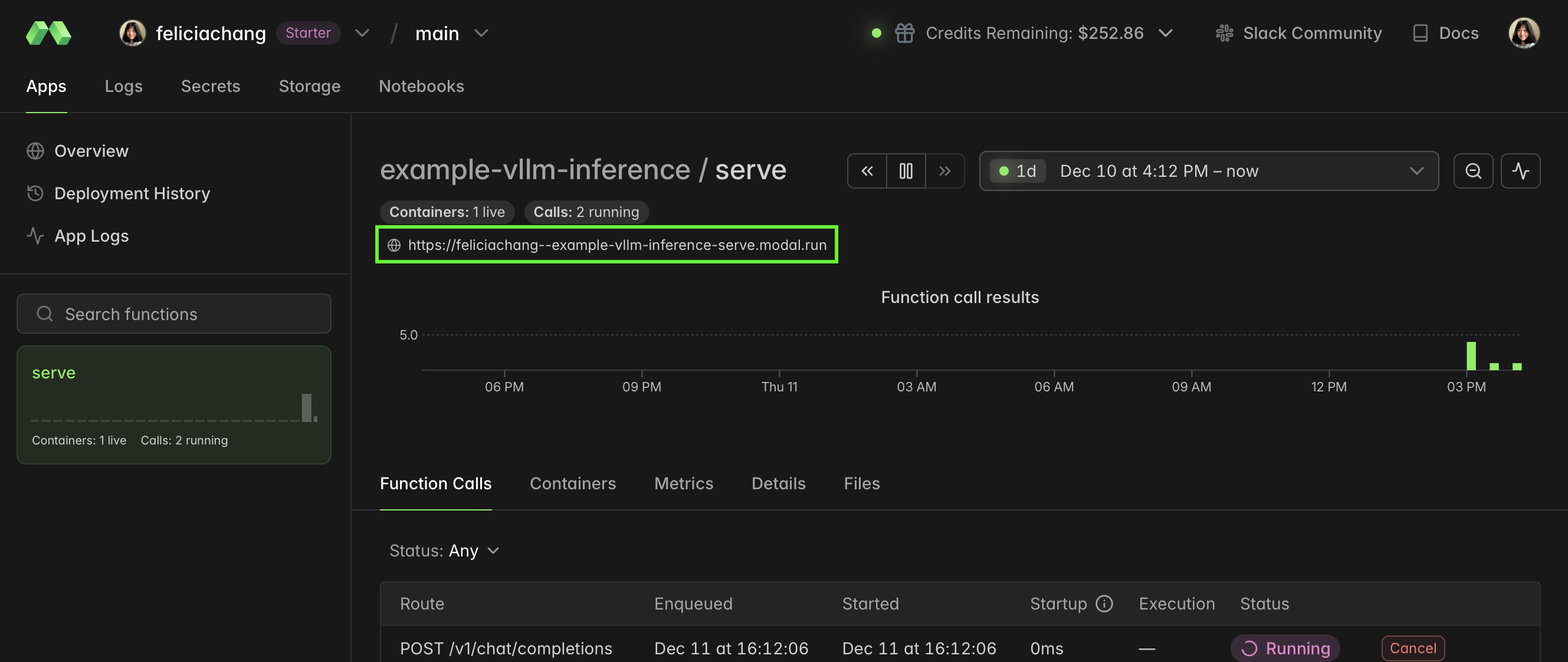
In the next step, we’ll work on connecting a Next.js app to Modal using the OpenAI Compatible Provider integration path in the AI SDK.
2. Connect a Next.js app to Modal with the Vercel AI SDK
Now on to the frontend! Start by creating a Next.js app using the defaults. If needed, install node and npm first.
Then install the OpenAI Compatible provider from the AI SDK, which we will use to connect to the Qwen 3 8B model running on Modal:
In the app folder, create a /chat route by creating an app/api/chat/route.ts file (note that route.ts lives in a few nested folders!). Then paste the following code:
Make sure to to change the parameters in the baseURL to match the URL output from the command line in the earlier step. It should look something like https://your-workspace-name--example-vllm-inference-serve.modal.run. We want to access the /v1 endpoint.
3. Add a chat UI with Vercel’s AI Elements
Then, using AI Elements, we can use out-of-the-box UI elements to create a chat interface.
Start with installing AI Elements and the AI SDK Dependencies:
Replace the code in app/page.tsx with the code in this Github Gist. It’s a long piece of code that provides a complete chat UI using AI Elements and sends user messages to the /api/chat endpoint. Most of it comes directly from the Next.js chatbot tutorial.
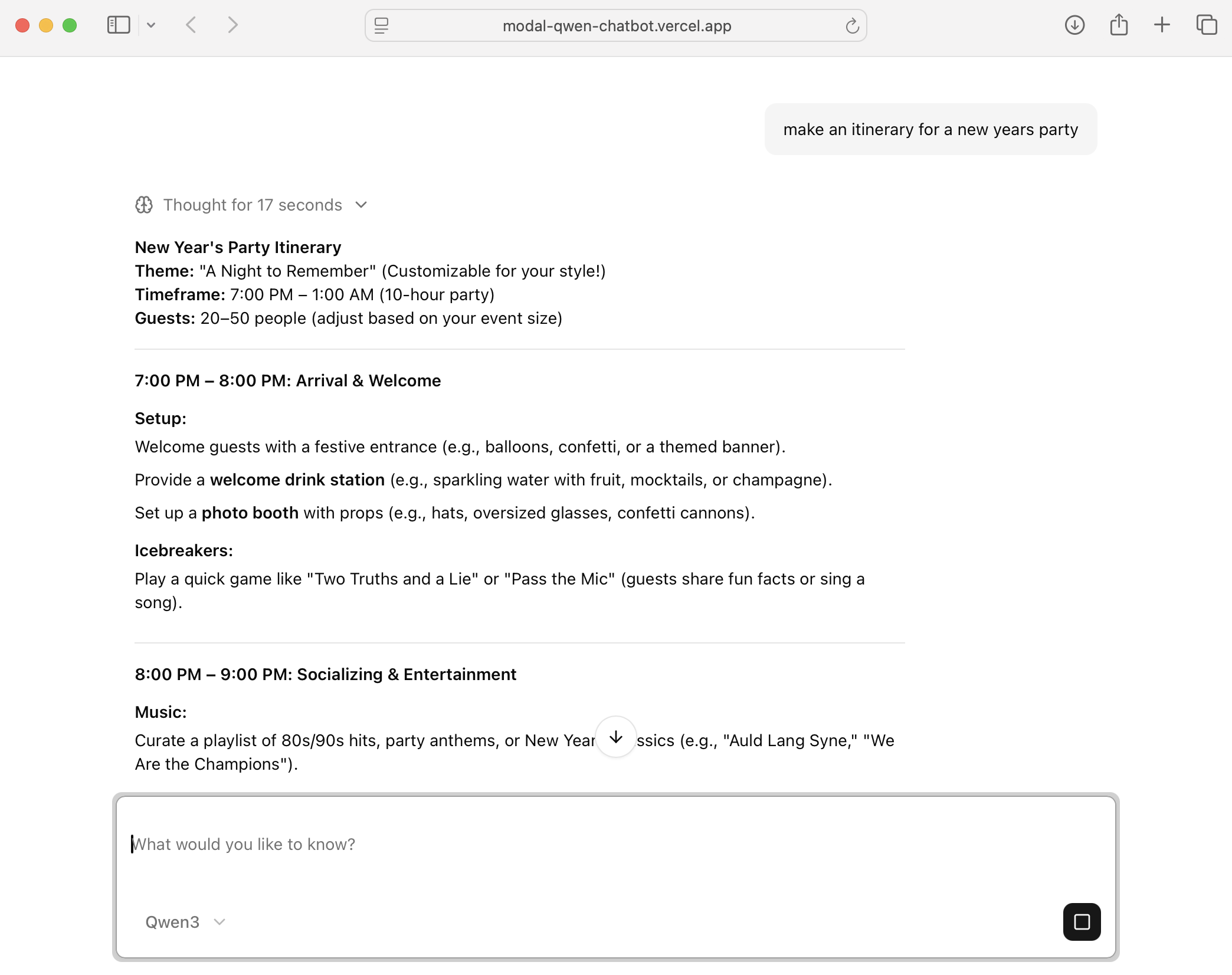
Now, you can play with a fully-fledged chatbot running the Qwen 3 8B model by running the following command:
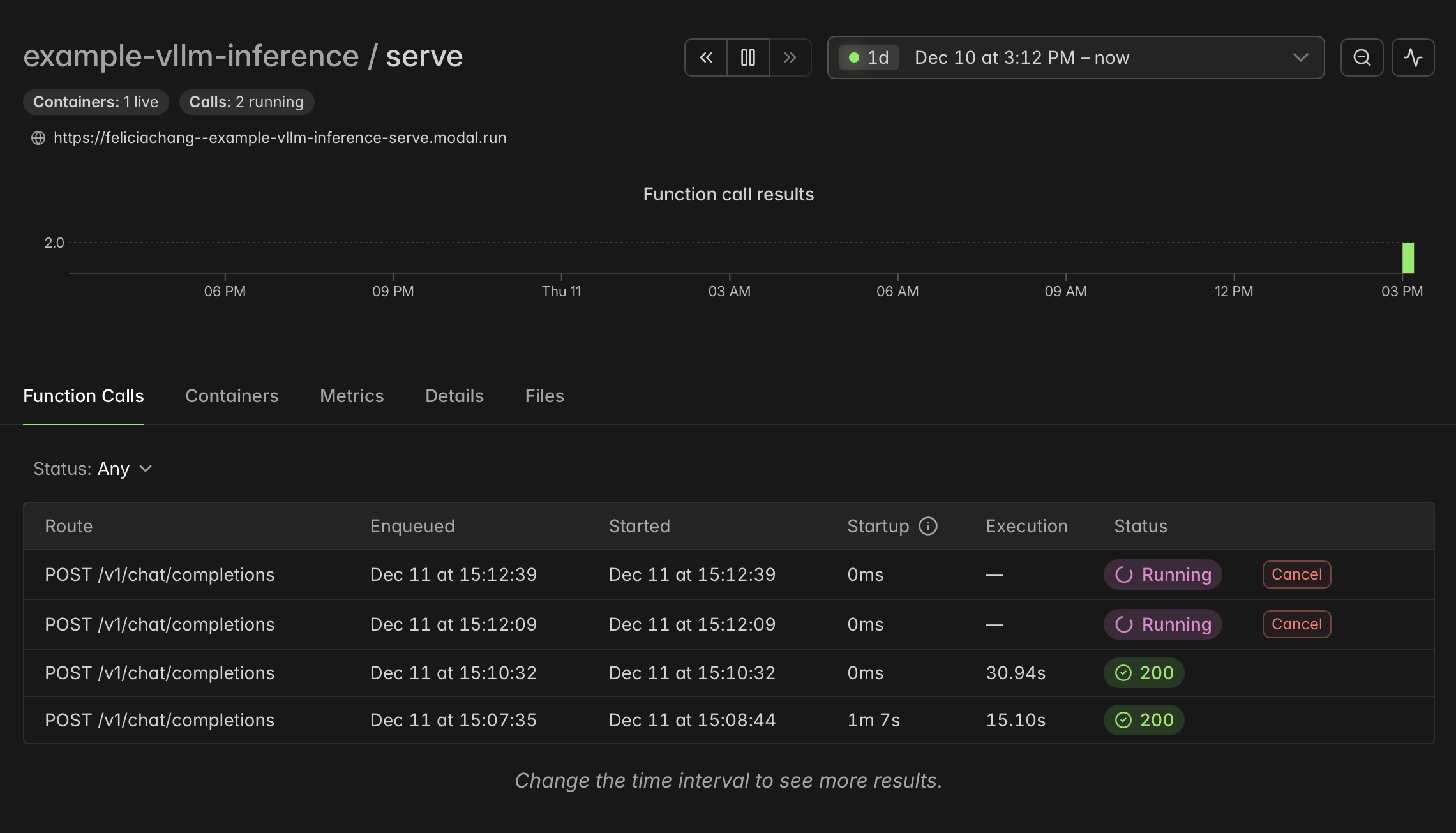
In the Modal dashboard, you can see that your queries trigger function calls:
For next steps, check out snapshotting GPU memory to speed up cold starts on Modal. For questions, join our Slack Community.